During the pandemic caused by the coronavirus, there was a collapse of health centers. At that time, face-to-face healthcare was limited to extremely serious or urgent cases. This situation highlighted the need to promote telemedicine, an option that, thanks to technology, opens up new options for medical care and telematic monitoring both in health centers and hospitals.
A study carried out by ESADE and the Barcelona Health Hub shows that during the pandemic almost 100% of scheduled medical visits were carried out via telemedicine. In fact, in April 2020, 85% of outpatient consultations in many hospitals were done by phone.
The same study reveals that once the pandemic is over, telemedicine will continue to form part of our day-to-day lives, reaching between 40 and 75% of visits. If it is true that this new form of medical assistance is here to stay, it is important to know what telemedicine is, what are its characteristics and advantages and basic aspects of hospital safety for the proper functioning of distance medicine.
What is telemedicine?
Telemedicine means, as the word itself indicates, distance medicine. Therefore, it consists of using information technologies (ICT) in healthcare, whether to make a diagnosis, monitor or treat the patient remotely.
“The telemedicine is about offering health services at a distance, without the need to be physically present in a health center or hospital.”

Types of telemedicine
Although telemedicine is often referred to as a general concept, the reality is that there are different types of distance medicine. Specifically, three types:
1. Remote patient monitoring
It refers to the remote control of patients with chronic diseases. Thanks to devices that collect data and vital signs on the health and condition of the patient, it is possible to monitor the patient from the hospital and take any action if necessary.
For example: In a patient with diabetes, blood sugar levels can be measured and, if it is too high, act.
2. Storage and shipping technologies
Allows you to store clinical data and send it to other centers.
For example: thanks to telemedicine, the specialist can consult the results of an X-ray image taken at the health center from his computer.
3. Interactive telemedicine
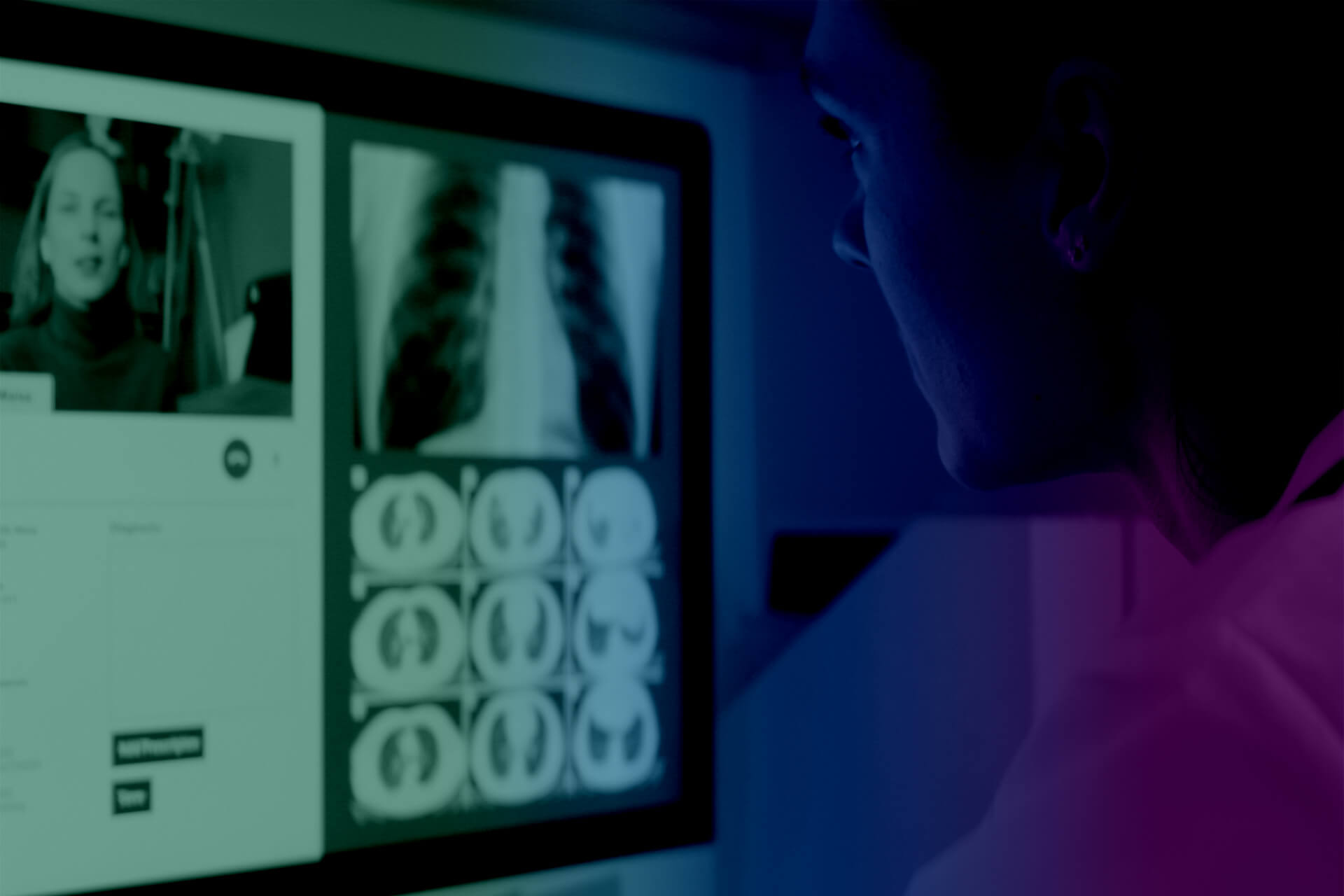
Facilitates real-time communication between doctor and patient without the need for both of them to be present at the medical consultation. It is usually done by video call while the patient is at home or, perhaps, at a nearby health center.
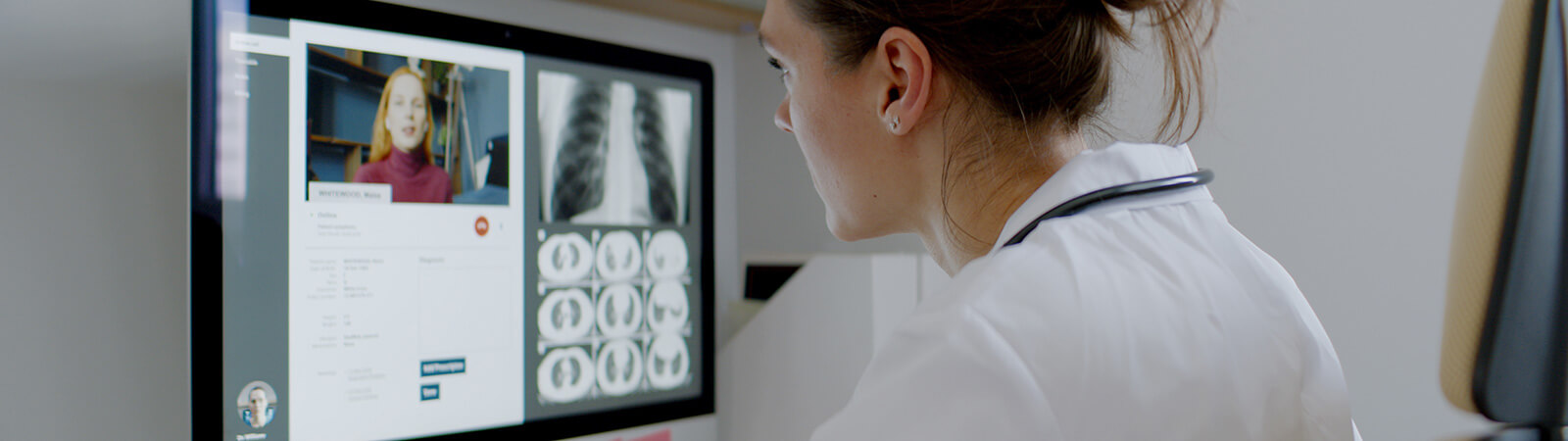
Advantages of distance medicine
Although the main advantage of distance medicine is the fact of being able to receive medical assistance without having to go to the health center, other factors must also be highlighted:
- It allows interactive and real-time remote communication between healthcare professionals and patients.
- Provides quick and convenient access to the health system.
- It is more efficient in terms of time and resources.
- Facilitates direct communication between different specialists.
- There is the possibility of making quick inquiries.
- Focused on covid-19: telemedicine avoids contacts, crowds and more risk of contagion.
- Waiting times and lists are reduced. For example, all consultations that are for sick leave, receive results or update prescriptions can be done virtually in less time.
Examples of telemedicine
Primary care consultations by phone
Telephone health care consultations are probably the most basic virtual medicine service. During the pandemic, these types of consultations have multiplied and, in fact, more and more health centers carry out the first consultation with the doctor by telephone.
Once the doctor knows the patient’s symptoms, he decides if a visit in person is necessary and makes an appointment with the person at a specific time when he or she can attend, thus avoiding crowding in waiting rooms, something essential in times of pandemic.
Mobile apps and medicine kits
The majority of telemedicine consultations in the public sphere are usually, as we have mentioned, by telephone call. However, private practices are leading the way in the application of remote medicine, using new technologies and artificial intelligence.
There are consultations, for example, that use applications to make video consultations with medical and healthcare professionals from anywhere. This is the case of the Ever Health app used by more than 200 schools, colleges and geriatric residences in Spain.
The private centers that use this application also have a personalized telemedicine kit. For example, in schools this kit includes a stethoscope. In this way, the doctor indicates where to place it and it is as if the patient were in consultation. Thanks to the use of this type of kit with thermometers, visual examination cameras, blood pressure monitors, etc., it is possible to solve the vast majority of queries remotely.
Artificial intelligence for diagnosis
Another example of artificial intelligence applied to digital health is found in Mediktor. It is a tool that, through artificial intelligence, facilitates a clinical pre-diagnosis, evaluating the patient’s health.
In this case, the tool acts as a medical assistant doing triage and pre-diagnosis, thus directing the patient to the appropriate level of medical care. The tool covers about 850 diseases, 3500 categorizations and 35,000 synonyms for the definition of symptoms that we use in our natural language.
The recommendation is based on an extensive medical bibliography and has been clinically validated, with a 91.3% correctness.
The future of telemedicine in Spain
In recent months we have seen how the coronavirus has opened the doors to greater use of telemedicine, especially by primary care centers. It has been the most useful way to avoid health collapse without reducing medical care. However, although we are seeing an advance in remote medicine, the reality is that there is still a long way to go.
According to data from HiMSS Analytics, in Europe only 16% of healthcare personnel work with artificial intelligence. In the case of Spain, the figures are even lower: only 11%, data that reveal that the application of technology in the field of health is still slow in our country.
On the other hand, telemedicine in Spain still lacks development and regulation. Our French, German and English neighbors have taken clear steps to develop distance medicine. For example, Germany has a Digital Health Law that penalizes those who do not offer virtual medicine services.

Hospital electrical safety applied to remote medicine
There is no doubt that the development of telemedicine has been possible thanks to the evolution and advancement of information and communication technologies in the health sector, in addition to the use of mobile phones, computers and the Internet in the home.
In this context, it is very important to take into account that virtual medicine depends exclusively on the proper functioning of technology and electricity. Therefore, in the use of remote medicine, it is recommended that medical centers and hospitals have advice on electrical safety to ensure that they have a hospital electrical safety system and tools that guarantee the provision of the service also in the event of adverse events or loss of power supply, for example.