For decades, the implementation of technology in the different spheres of human life has transformed the way we consume, relate to each other and live. It has certainly transformed it for the better. After all, a priori, technology makes our lives easier. However, as we use more and more electronic systems in our daily lives, we also become more energy dependent.
That is why, in a field such as healthcare, the use of batteries for emergency supply units in hospitals is essential to guarantee permanent access to the power supply, even in the most complicated situations or in exceptional events that may cause, for example, power cuts.
Today we want to address the importance of batteries and uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) for the proper functioning of the healthcare system.
What is a UPS?
We cannot start talking about batteries without first taking a moment to define and understand what an uninterruptible power supply is.
The complex hospital infrastructure means that these types of buildings dedicated to patient care and well-being constantly require a power supply to be able to carry out their work and continue to save lives, provide diagnoses, attend to patients, etc.
In this context, the UPS is responsible for ensuring that the electronic devices to which it is connected will be instantly powered under any circumstances, such as if there is a power interruption or power outage or if the power supply is above maximum safety levels.
“The UPS provides power through the use of a clean battery backup that also protects the equipment connected to the system from surges.”
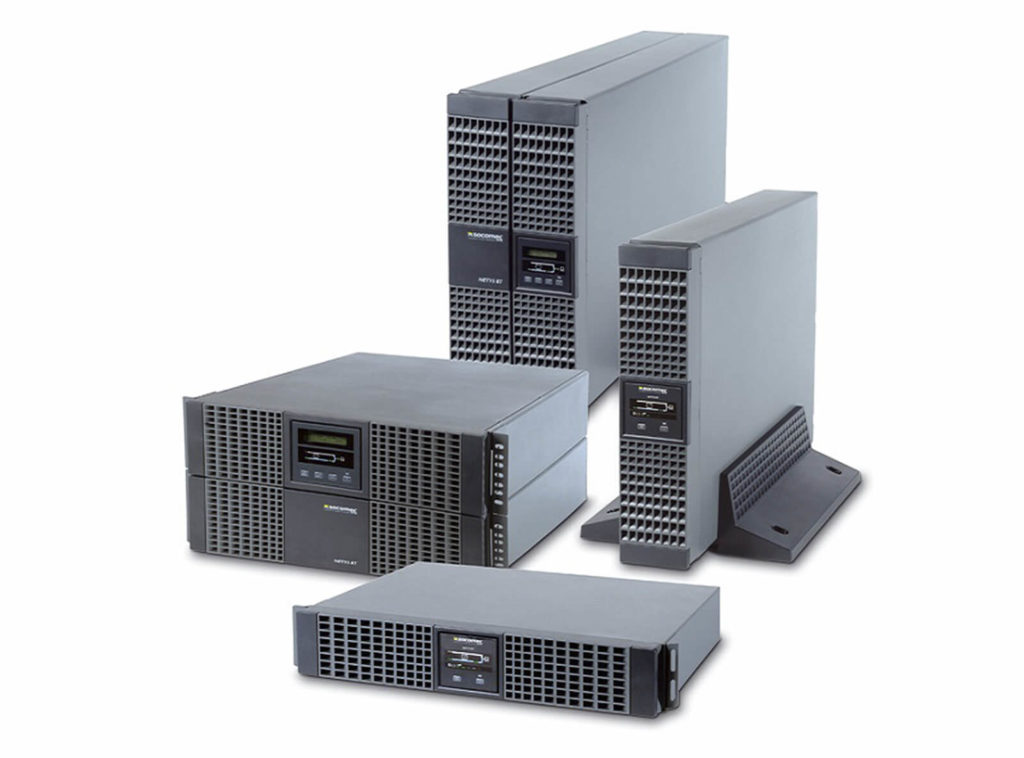

Why is a UPS important?
If a power outage occurs in a hospital, shutting down electronic equipment and systems, it can put the lives of many people at risk. When a power outage occurs, although most systems are ready to recover and provide power again, sometimes it can take up to a minute to connect to the generator or a new emergency generator, a time that in the hospital environment is precious and can mean the difference between life and death.
Given how delicate and dangerous it can be for a hospital to be left without a power supply, the SIA system, known as UPS (uninterruptible power supply) is one of the devices that no one expects to have to use in the hospital, but it is mandatory because it can save lives by preventing vital equipment such as anaesthesia machines or ventilators from shutting down.

Here are some other examples that highlight the importance of having UPS systems in hospitals, ensuring hospital electrical safety:
- A UPS gives confidence and efficiency to a hospital centre as it guarantees the electrical system in any circumstance.
- It integrates localised battery backup functions and UPS systems throughout the hospital, thus facilitating the simplification of operations.
- A central UPS system reduces system downtime, maintenance time and operations, thus contributing to cost reduction in the hospital.
When is a UPS needed?
Most commonly, these systems are used to supply power when the mains supply fails for a “short” interval of time and until the mains supply is restored. However, uninterruptible power supplies or UPSs can also be used for other types of power supply problems:
Power outages
Power surges, voltage surges or spikes.
Electrical or electromagnetic noise.
Unstable frequency
In this context, it is worth noting that not all UPS systems are the same, but are often built according to the electrical faults or problems they seek to correct. For example, it is possible to have UPS equipment that regulates voltage, but also prevents electrical overload.
What are the components of a UPS system?
Although the main mission of the UPS is to provide power supply, this system has two parallel circuits:
- A circuit dedicated to receiving the current to power the electronic devices connected to the system.
- Another circuit is dedicated to charging the battery that keeps the devices running in the event of a power failure or power cut.
On this basis, the UPS system has several components with different functionalities:
Battery
This is the heart of the system, the most important element. Without a powerful battery, the device does not work. Moreover, the battery life has a direct impact on the life of the system and its capacity is what determines the efficiency and autonomy time of the UPS system.
The battery rectifier
It is mainly responsible for two functions. On the one hand, it transforms alternating current into direct current so that the battery can be recharged. On the other hand, the rectifier acts as a protective “wall” preventing the pure current from directly impacting the feeder.
The inverter
This is another vital component of the UPS system in that when the power from the power line is interrupted, the battery is activated, in turn activating the alternator and starting up the energy storage system that is used for medical and electronic equipment. This device, as the DC power builds up in the battery, transforms it into AC power very similar to the mains power, but ensures that it is filtered and will not cause any voltage spikes. It therefore ensures that the UPS provides safe power.
The filter
Its function is to transform the mains pulses into sinusoidal type power. By acting as a filter, it facilitates the energy efficiency and lifetime of the UPS device.
Batteries for emergency power supply units
Now that we know that the battery is one of the most important components of a UPS system, it is time to learn a little more about this type of device that converts the energy it stores into electrical current.
First of all, there are some basic aspects to know about the batteries of any UPS system:
- You have to know how long the standby time is.
- Know the charge and discharge cycles.
- Batteries are usually lead-acid batteries, which are safer because they are leak-proof.
- They are used as backup batteries, so it is important to know the volts and amps it is capable of supplying to the UPS system.
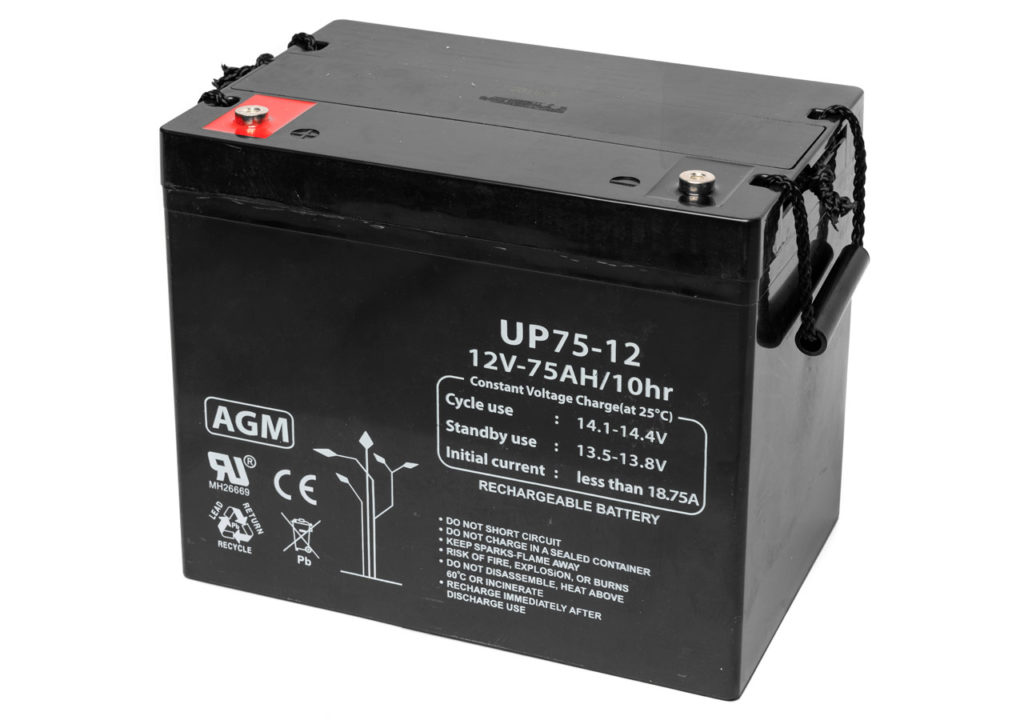

Types of AGM batteries for medical use
At ETKHO we have different types of batteries for emergency supply units.
The batteries mentioned below are high discharge lead acid batteries (12 volts) with a current range from 7.0 to 90A. They use AGM technology, i.e. they allow the electrolyte to remain stationary while in contact with the active lead material in the plates for consistent performance and durability.
ETK BAT 7.0-12 AGM
12 Volt 7.0 Amp high discharge lead acid battery
ETK BAT 40-12 AGM
High discharge lead acid battery 12 Volt 40 Amp
ETK BAT 50-12 AGM
High discharge lead acid battery 12 Volts 50 Amp
ETK BAT 90-12 AGM
High discharge lead acid battery 12 Volt 90 Amp
With this article you already have the basic and essential knowledge about batteries for emergency supply units in hospitals. However, if you are still in any doubt, our team of hospital electrical safety specialists can offer you advice to ensure you make a safe and efficient choice.



