Proton therapy is a very specific type of radiotherapy and much more effective, precise and safe for certain cases of cancer, which has led it to become a powerful tool in the fight against this disease.
While conventional radiotherapy uses photons or electrons, this therapy uses protons to treat malignant tumors.
In this article we are going to see in detail what proton therapy is, the advantages and benefits it offers, the challenges it presents and what situation it is in.
What is proton therapy?
It is an advanced form of radiation therapy that uses positively charged protons instead of x-ray radiation.
The protons release their energy in a controlled and precise manner into the target tissue, making this technique especially effective in treating cancer.
Another of the most notable aspects of this therapy lies in the fact that the protons deposit most of their energy in the tumor and then stop, avoiding significant damage to the surrounding healthy tissue.
Overcoming the results of radiotherapy
Proton therapy has a more efficient distribution of energy than photons, making it possible to direct higher doses to the tumor area.
Furthermore, it does so without increasing doses in other areas, minimizing the damage that can occur in healthy or very sensitive tissues.
In this sense, this treatment is considered the best choice for children with cancer because it respects growing tissues, reducing sequelae, something essential for the child’s future development.
In fact, the majority of minors treated with proton therapy are cured and will have fewer sequelae.
In addition to pediatric tumors, proton therapy provides very promising results with minimal side effects in skull base tumors, ocular melanoma or lymphomas, among others.

Proton therapy in Spain: good foundations and a way to go
This radiotherapy has been gaining notable recognition and acceptance among the Spanish medical and scientific community.
However, there are only two centers with proton therapy in Spain: the Quirónsalud Protontherapy Center and the Cancer Center Clínica Universidad de Navarra.
Both private.
The two centers, references in this area for the rest of the National Health System, have been operational for more than three years, demonstrating their effectiveness as an advanced, safe and effective therapy in the treatment of different tumors.
In fact, until December 2019, proton therapy treatment was not carried out in Spain. It represented a historic advance in the fight against cancer in our country.
Worldwide, it is estimated that more than 140,000 patients have already been treated with this therapy.
Development in public health
In a few years, proton therapy in public healthcare will be a reality.
The therapy will be offered within the National Health System thanks in part to the donation of 280 million euros made by Amancio Ortega in October 2021.
Currently there are ten teams already tendered for this. But they are not even manufactured yet.
The reason? The time factor.
According to the Spanish Society of Radiation Oncology (SEOR), it takes at least three years to launch them. And according to NIUS, the manufacturing, installation and preparation of the equipment is complex because they are authentic bunkers.
Not all hospitals are suitable to accommodate them.
Radioactive facilities require permits from the Nuclear Safety Council and ample space because they are about the size of a tennis court. In addition, healthcare personnel must be trained so that they are prepared at the same time as the machine.
For all of the above, this state-of-the-art medical equipment is expected to operate in public health centers from 2024-2025.
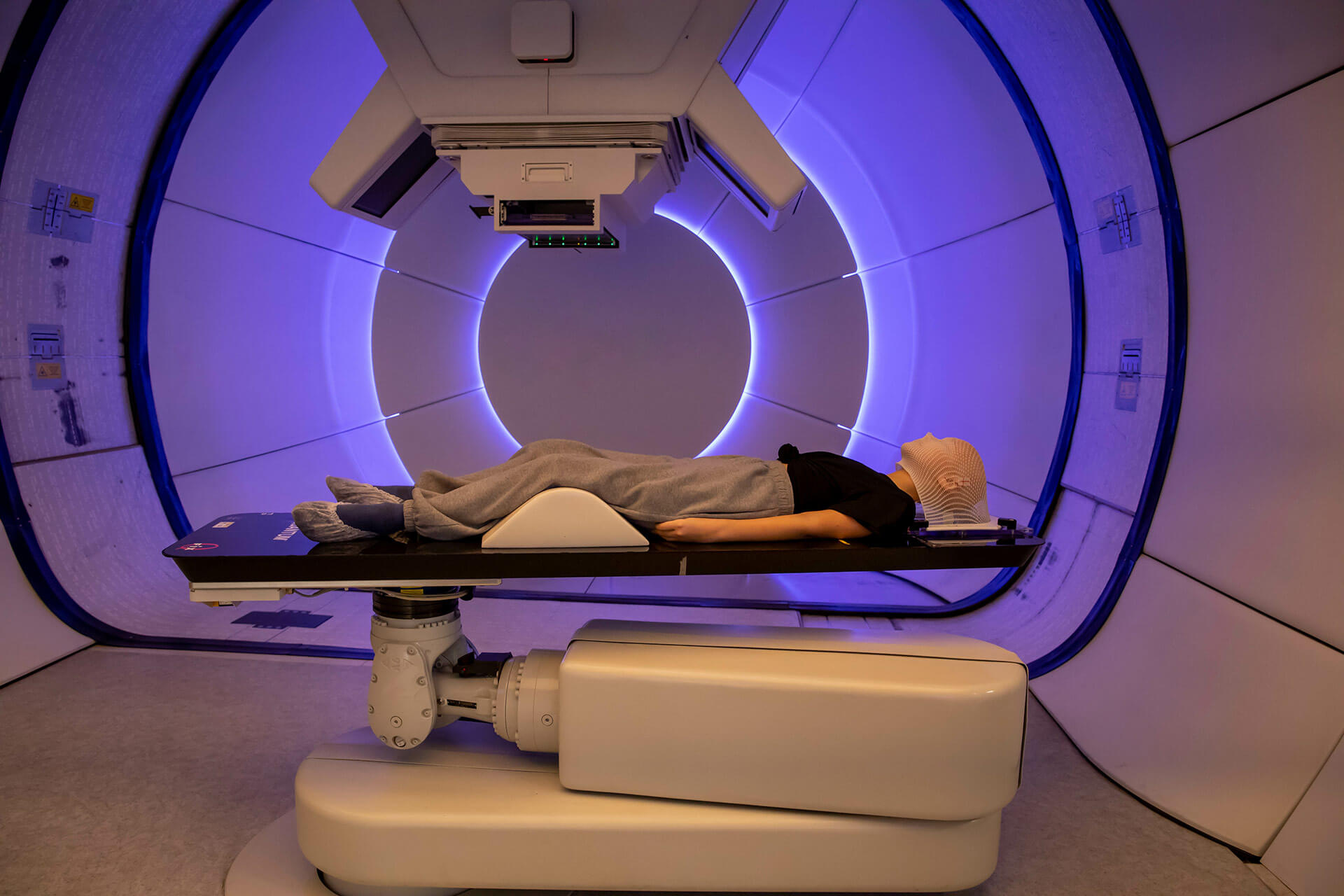
What is the treatment like? Side effects and advantages
If proton therapy has fewer side effects, it is because it causes less toxicity in the irradiated area.
In general, the side effects associated with this type of cancer treatment will depend on the interaction between the irradiation itself in the tissues and the general condition of the patient and the tissues exposed to radiation.
The most well-known effects include:
- fatigue
- skin irritation
- loss of appetite
- nausea and vomiting
- hair loss
However, the expected toxicity of each radiotherapy treatment is individualized and very predictable.
On the other hand, compared to conventional radiotherapy or external beam radiotherapy (EBRT), proton treatment offers several advantages that we mention below.
Greater precision
Its ability to deliver highly precise radiation doses to the tumor minimizes damage to surrounding tissues.
This is especially valuable in the treatment of tumors near critical organs or in pediatric patients, where minimizing long-term side effects is essential because it reduces the risk of damage to surrounding healthy tissues and organs.
Reduction of side effects
Proton therapy tends to cause fewer side effects compared to more conventional treatments.
This significantly improves the quality of life of patients during and after treatment. Patients may experience less skin irritation, fatigue, and other symptoms associated with radiation.
Suitable for resistant tumors
Proton therapy is effective in the treatment of tumors resistant to conventional radiotherapy.
The ability to increase the dose to the target tumor without significantly increasing the risk of side effects allows challenging clinical cases to be addressed.
Potential to reduce the risk of second tumors
Due to its precision and ability to minimize radiation exposure to healthy tissues, it has been suggested that proton therapy may reduce the risk of developing radiation-related second tumors compared to conventional radiation therapy.
Lower risk of radiation to healthy tissues and organs
Proton therapy facilitates a more focused distribution of the radiation dose, reducing the amount of radiation received by healthy tissues and organs near the tumor.
Shorter and more effective treatment
Proton therapy requires fewer treatment sessions and may be especially beneficial in treating certain types of cancer such as:
- brain tumors
- pediatric tumors
- tumors at the base of the skull
- head and neck tumors
- prostate tumors
The challenges of proton therapy
While proton therapy has many benefits, it is not suitable for all patients and is not yet available in all centers.
That is perhaps its main handicap.
And that’s also why it’s crucial for patients to consult their doctor to determine if proton therapy is right for their particular case.
Other proton therapy challenges and issues that need to be addressed include:
- The selection of appropriate cases: This is essential to ensure that this technique is used effectively and efficiently.
- The high cost: One of the biggest obstacles to the widespread adoption of proton therapy is its high price. Building and operating a proton therapy center are financially demanding.
- The limited scientific evidence: Although significant research has been carried out on proton therapy, there is still no literature as extensive as that of conventional radiotherapy.
- ‘Restricted’ access: Although we have made progress in the availability of this type of therapy, there are still challenges in terms of geographic accessibility.
In summary, proton therapy represents a significant advance in cancer treatment, offering greater precision and reduction of side effects compared to conventional radiotherapy.
Its growth in Spain and around the world is promising.
Additionally, continued research and efforts to make proton therapy more accessible are crucial to fully realizing its potential in the fight against cancer.



