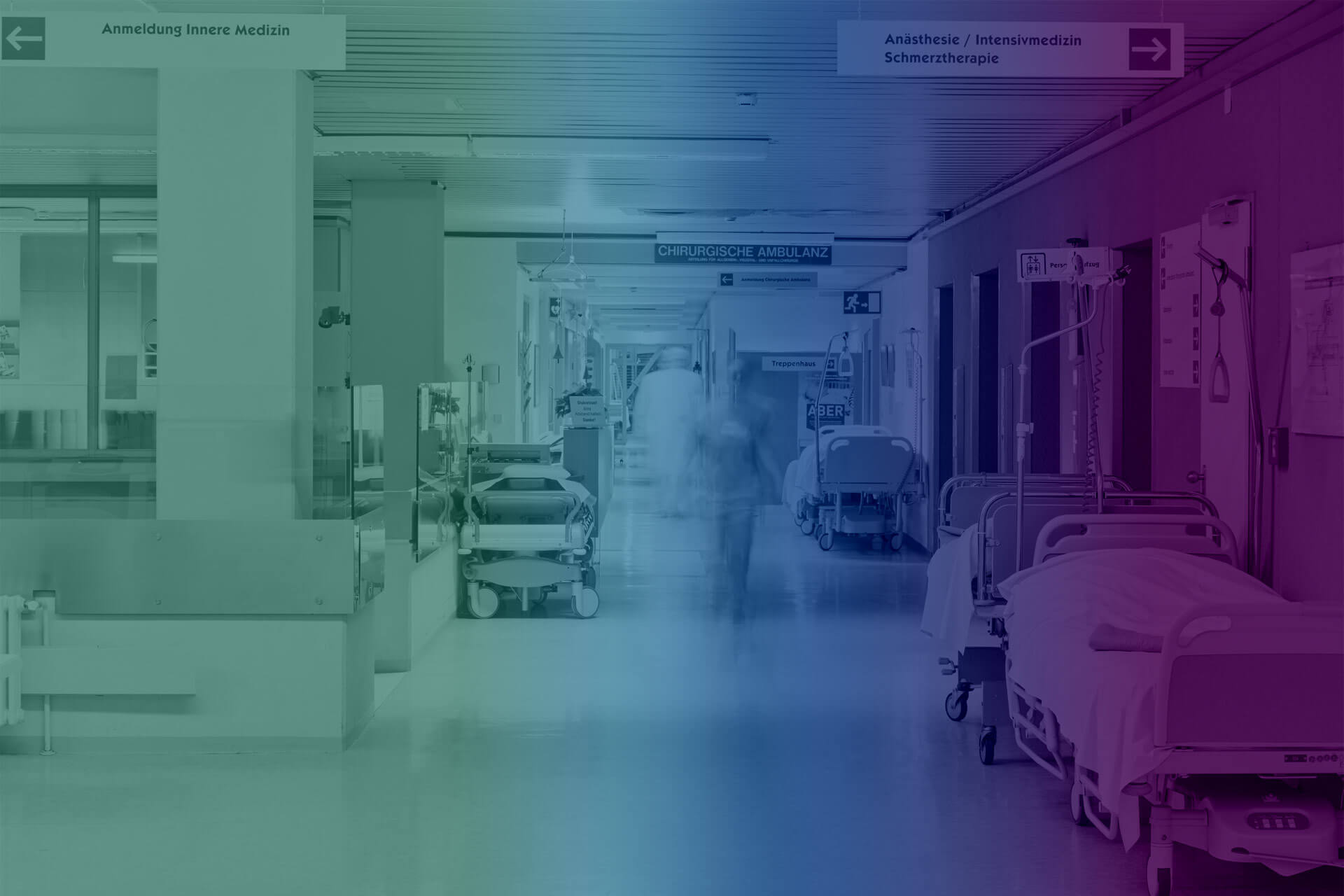
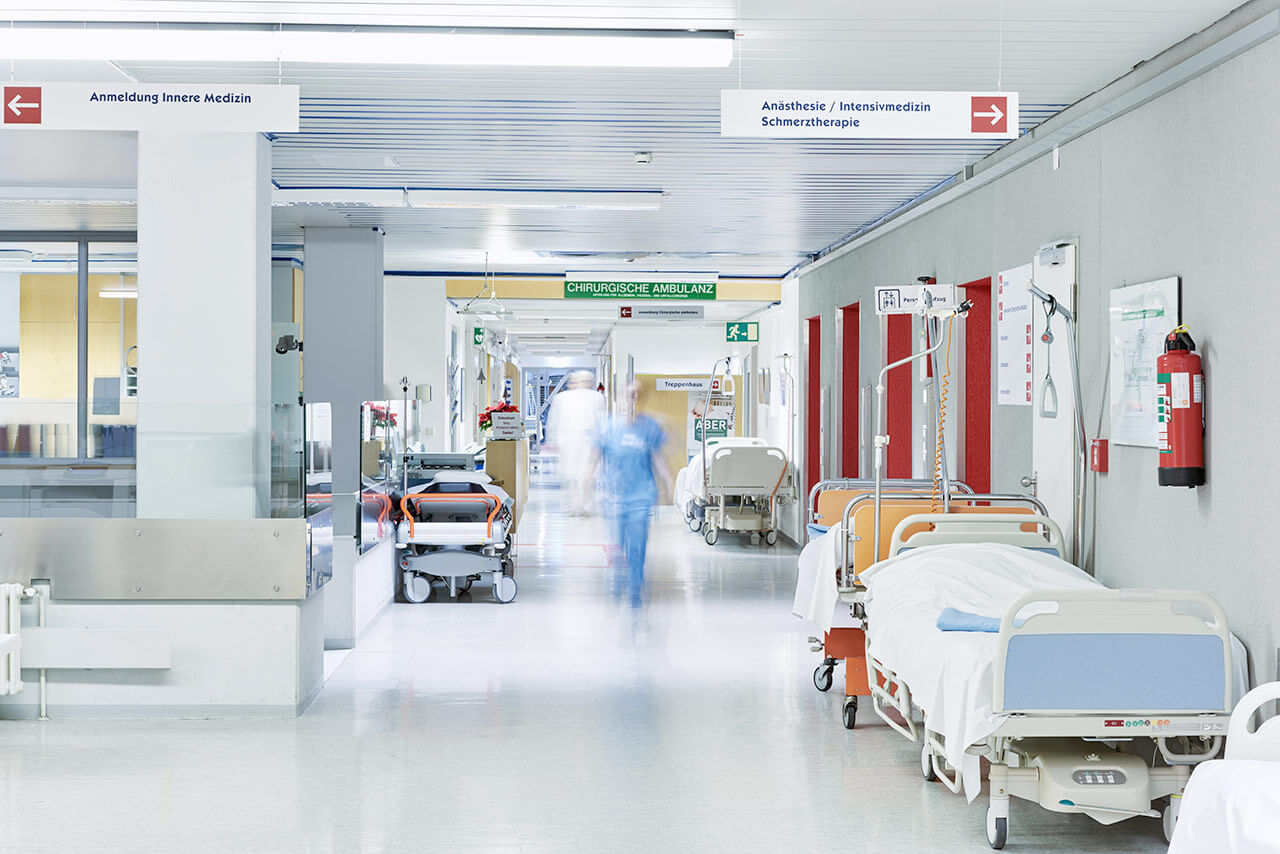
Patients, services, specialties, types of units, medical equipment … In the design and organization of critical hospital areas, a whole series of aspects must be assessed to guarantee the safety and proper functioning of the health center.
There are infinite options to define the different types of health centers: depending on their size, the services they provide,… However, in a generic way, we can define a hospital as a building where functions related to people’s health are carried out , in addition to the diagnosis and treatment of diseases. Each hospital has its peculiarities. However, there are some basic aspects about the design and organization of critical hospital areas that are important to assess.

Why is the architecture and design of a hospital so important?
The architecture and design of a health center is not a trivial matter. It is a complex designed for the care of people with health problems.
The structure and layout of a hospital is classified based on the tasks carried out within it. There are different types of spaces: waiting rooms, operating rooms, palliative care, etc.
Each of these areas has a function and requirements. And that is precisely what makes hospitals a complex type of building in terms of design and construction, as it must be adapted to different medical and professional services and disciplines.
In the construction of hospitals, aspects that go beyond mere design must be considered: distribution, utility, materials and also aesthetics. All this contributes to, for example, guaranteeing the existence of aseptic spaces or suitable environments for the well-being and quality of care for the patient during their admission
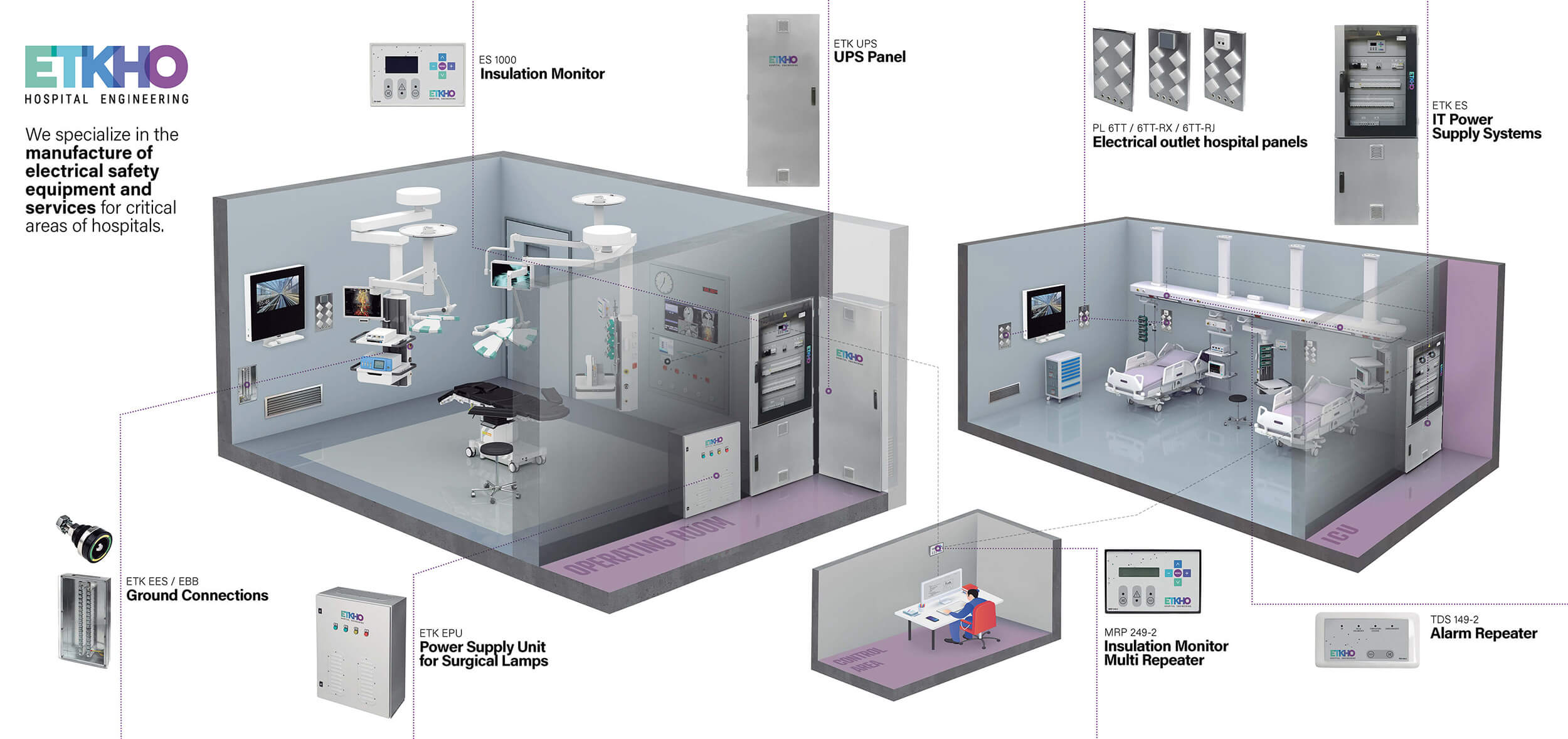
Design of critical hospital areas
One of the most important areas when building a hospital is the design of critical hospital areas. The structure and design of this space directly influences the functionality of the critical areas, their safety and efficiency.
Basics
Hospital design and construction has evolved as technology has. In this way, it has been possible to incorporate elements in hospitals to improve their usefulness and effectiveness.
On the other hand, hospitals are made up of different units, services, etc., which often work together. Therefore, it is very important to study and create spaces in which mobility, synchrony and distance are perfectly adapted.
Nor should we forget other very important areas or systems such as hospital electrical safety, ventilation systems or the control and management of waste. In short, the safety and efficiency of hospitals begin from the design and construction phase of the same.
Each part of the design of a hospital must respond to health needs, possible emergencies or risks derived from natural disasters or problems in the electrical supply and the main functionality of a hospital: to serve patients safely and guaranteeing their well-being.
When talking about the basic design of hospitals and critical areas, a series of norms and quality standards must also be considered, such as the resistance of the structure, materials that facilitate and guarantee cleanliness and hygiene, air filtration or insulation of pipes and wiring.
Design according to the types of critical areas
- High-risk critical areas: These are operating rooms, ICU, surgery rooms, etc.
- Semi-critical areas: Refers to spaces in which analyzes are carried out. That is, labs, radiology, oncology, or the morgue.
One of the main characteristics of the design of hospital critical areas is the need to incorporate outlets for the use of medicinal gases and all kinds of connections for the necessary medical equipment and supplies. Likewise, aspects such as dilution, filtration (essential to avoid contagions and control infections), temperature, humidity or pressure must also be considered.
There are also non-critical areas that will have a different layout. In this case, they are usually the spaces for administrative functions, warehouse, dressing rooms, rest areas for doctors, laundry, etc.
Regardless of whether it is a critical area or not, the entire hospital layout and spaces must be clearly identified and marked. It is a way to facilitate movement around the building and avoid confusion or mistakes. In this sense, the most critical areas are also often isolated.

Organization of critical hospital areas
The structure of the critical areas is closely related to their operation and the organization of the hospital itself. In this sense, it is important:
- Consider the capacity of staff and patients that the facility can accommodate.
- Guarantee the conservation of temperature.
- Guarantee aseptic spaces.
- Guarantee the tightness of the different areas with the use of special stainless steel doors without cracks.
- Floors, ceilings and walls cannot be sectioned to prevent bacteria from accumulating in the joints. In addition, the materials to cover them cannot cause reflection or be luminous and must be resistant to fire.
To understand the different structures or ways of organizing a hospital, we must know 3 concepts:
1. Unit
It is an organized architectural space where certain functions and services are developed, which can be healthcare, analysis, administrative, etc. A hospital unit is usually linked to a specific function. For example: Hospitalization Unit. Oncology Unit, Maintenance Unit, etc.
2. Area
It is a space or area where technical functions or medical assistance are carried out. The area of a hospital can integrate different specialties or be individual. And it can include one or more organizational units. Critical areas such as the ICU or surgical rooms are an example, but there are also clinical office areas, among others.
3. System
This type of structure is related to a general function that is not assigned to a single territory but is present at different locations in the hospital. For example: the computer communication system, the hospital electrical security system, the filtration system, the air conditioning system, etc.
“The design and organization of hospital critical areas depends on many factors, but it should always have one main mission: to facilitate hospital medical care and to ensure the safety and quality of patient care.